Life in Vladimir Putin's Russia explained in 10 charts
Vladimir Putin has dominated Russian politics as its undisputed leader for almost two decades.
Over successive terms as president and prime minister he has overseen an economic boom, military expansion and the re-establishment of Russia as a major power.
Living standards for most Russians improved, and a renewed sense of stability and national pride emerged. But the price, many say, was the erosion of Russia's fledgling democracy.
How has life changed for ordinary Russians during this time?
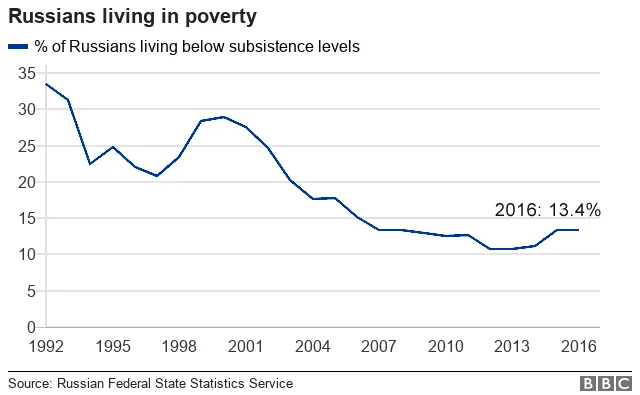
1. Fewer people are poor
Levels of poverty may be significantly lower than before, but Russia is still above the average for many of the world's biggest economies.
2. But wage growth has stalled recently
During Mr Putin's first stint as president, wages consistently grew by over 10% annually. Since returning to office in 2012, following a period as prime minister, significant growth has proved more elusive, with a series of crises and economic sanctions.
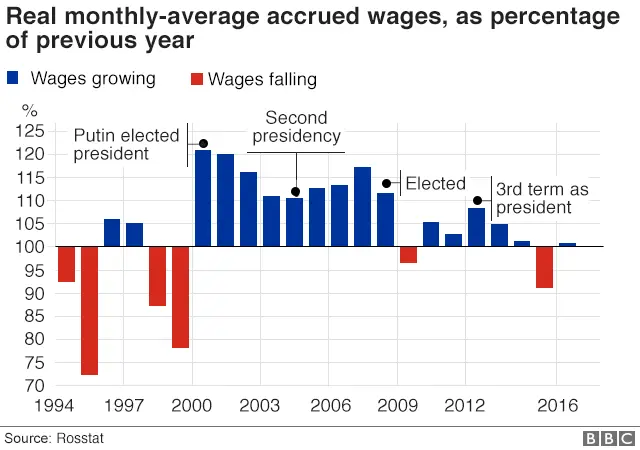
Between 2011 and 2014, disposable income grew by 11% and the Putin era has seen Russia's consumer economy expand considerably.
Read more:
3. More people have a car, and there are more microwaves than households
Russia's enduring love affair with the Lada continues, with Ladas accounting for 311,588 of the total 1,595,737 new cars sold in 2017.
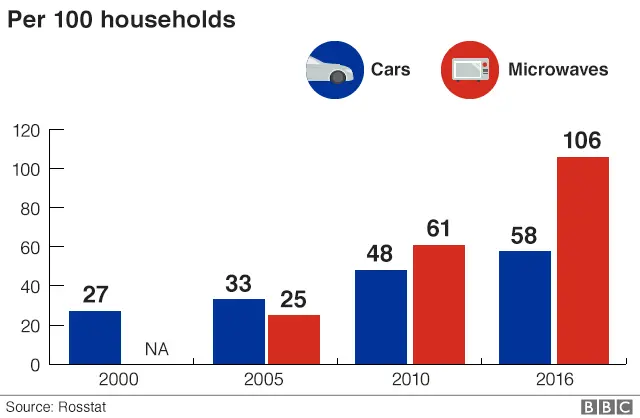
Car ownership in Russia is on a par with former Eastern Bloc countries Poland and Hungary, but some way behind its neighbour Finland which has 76 cars per 100 households, according to the European Automobile Manufacturers Association.
4. Russians fell in love with Ikea
Russia got its first store in 2000, as part of a MEGA branded shopping centre in Khimki, near Moscow. It went straight into Ikea's top 10 grossing stores worldwide.
By 2015, the country was the flat pack empire's second fastest growing market.
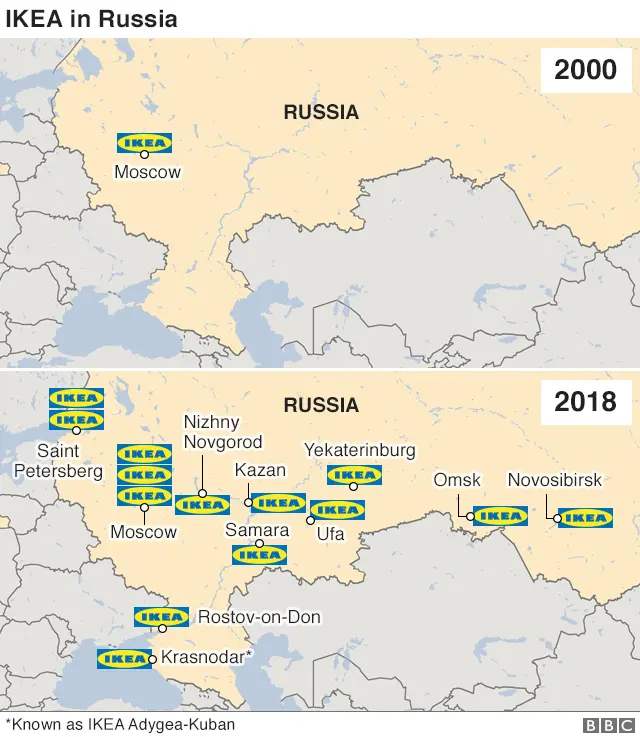

The company now has 14 stores across the country from St Petersburg to Novosibirsk, with three around Moscow alone.
It's not all been plain sailing. Ikea closed an online magazine over fears it could break Mr Putin's controversial law banning the promotion of gay values to minors; and it has also battled to maintain its strong anti-corruption ethics while operating in Russia.
5. And champagne...
There's some dispute over how much Russians drink.
Official figures show a drop, but not the 80% claimed by the health minister.
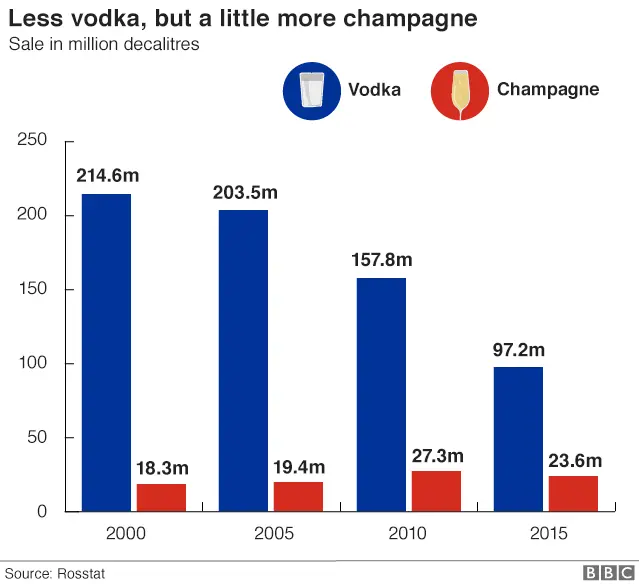
The decline in vodka drinking is in part down to the growth of a more "western" beer and wine culture. Beer was once considered almost a soft drink in Russia, but some oligarchs have now opened their own wineries.
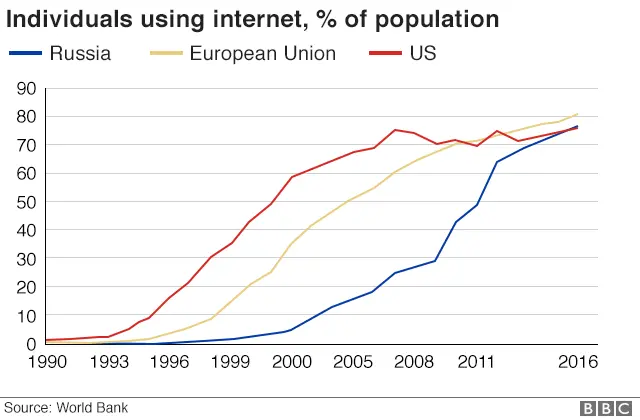
6. Like everywhere, the internet took off
The Russian internet has its own giants - the top site is social media platform VK (aka VKontakte) with around 90 million users compared to Facebook's 20 million, according to World Bank analysis.
Search engine Yandex occupies the second slot. Being built on Russian language and algorithms gives it a competitive advantage over Google.
7. But circuses are in decline
With more than 60 permanent venues across Russia circuses, like the Moscow State Circus, are a national institution. But they have faced strong competition from, and defections to, western rivals such as Cirque du Soleil.
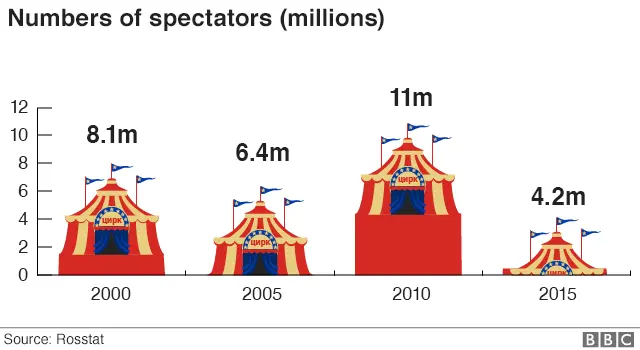
And from 2010, appetite for the circus spectacle dropped by a whopping 60%.
There's no single factor we could identify to explain the decline - changing tastes, rival attractions and growth of the internet are likely to have all played a role.
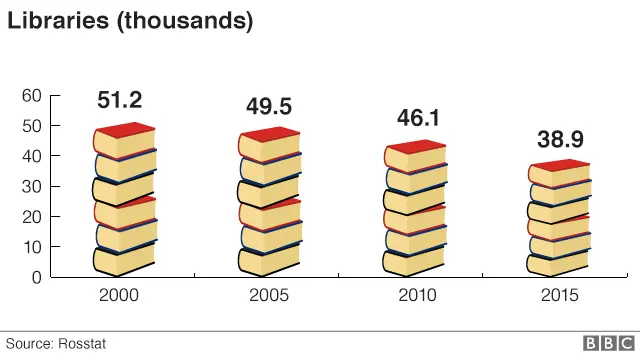
8. And so are public libraries
Much like everywhere else, the humble library has declined as access to the web has exploded.
 AFP
AFP9. Russia's population is growing again
One of President Putin's big goals is to turn around the dramatic population decline which began around the time of the ending of communism in 1991.
Before he ran again as president in 2012, Mr Putin proposed spending 1.5tn roubles ($53bn; £33bn) on raising the birth rate.
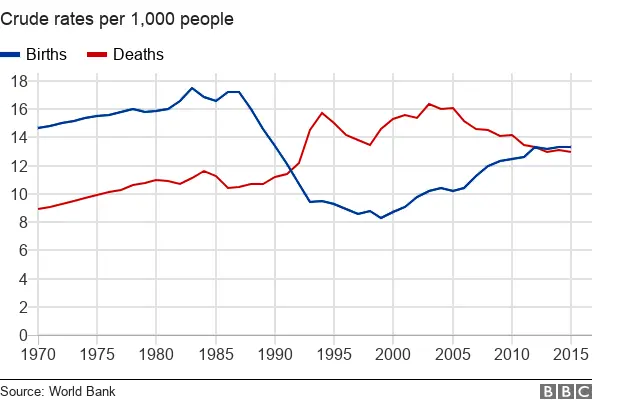
Probably by coincidence, 2012 saw Russia's birth rate exceed the death rate for the first time in 21 years.
When it dropped off in 2017, Mr Putin's opponents saw a chance to attack, highlighting a fall of 10.6% between 2016 and 2017 - in reality a change from 12.9 to 11.5 births per thousand people.
The highest birth rates are in Caucasus republics, such as Chechnya and Dagestan, while the most popular names for babies born in Moscow are Alexander and Sofia.
10. And Putin is spending more than ever on the military
A strong military has always been a key part of Russia's national identity, but the Soviet Union effectively bankrupted itself in an effort to match the United States during the Cold War.
The Soviet Union's collapse plunged the armed forces into penury as budgets were slashed. Equipment and weaponry became decrepit, and morale plunged.
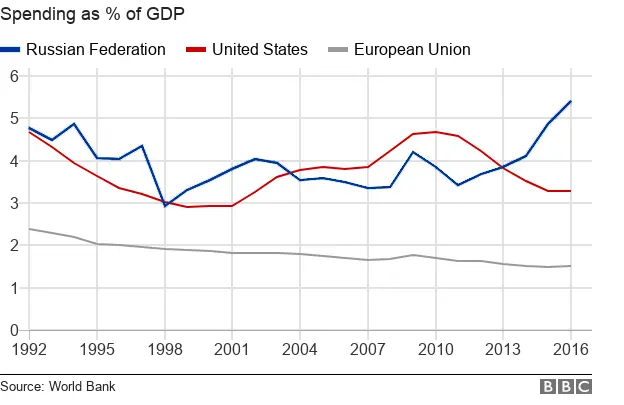
Vladimir Putin gave early intent to reverse this decline and rebuild Russia as a modern military force.
A series of modernisation drives have seen spending as a percentage of GDP almost double.
And Mr Putin's time in office has seen Russia flex its military might in Chechnya, Georgia, eastern Ukraine and most recently Syria.
Produced by: Alex Murray, Tom Housden
Analysis: Anastasia Napalkova, BBC Russian
Graphic design: Sandra Rodriguez Chillida, Joy Roxas, Zoe Bartholomew
