Manchester Arena attack: Key failings of emergency response
 Family handouts
Family handoutsThe Manchester Arena Inquiry has published a catalogue of failings and mistakes by the emergency services following the terror attack in 2017.
Chairman Sir John Saunders highlighted a number of failures of the emergency response to the suicide bombing and said avoidable mistakes had been made.
Here are some of the key failings.
1. No-one declared a major incident
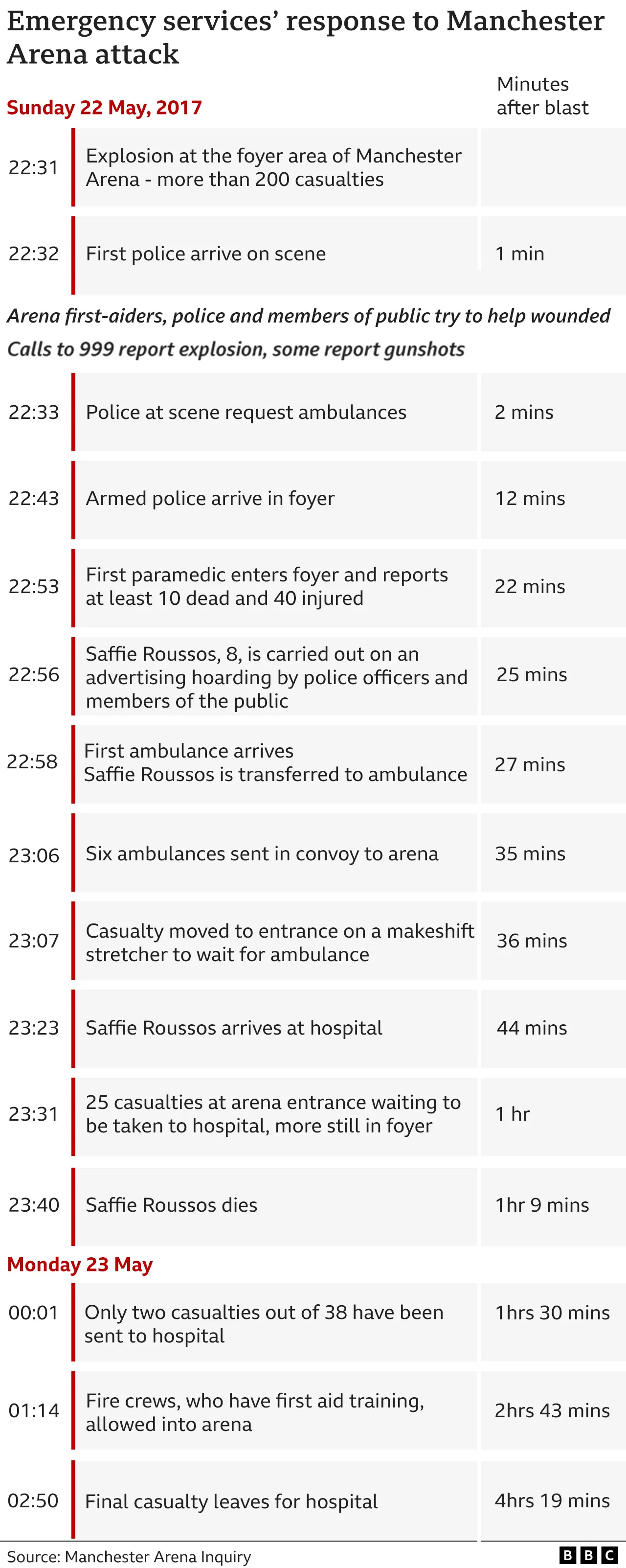
Sir John said the police inspector in initial command of the Manchester Arena bombing response "quickly became overburdened by the number of tasks he had to undertake" and it led to a "direct impact on the effectiveness" of the response.
Insp Dale Sexton failed to tell other emergency services he had declared Operation Plato - a pre-arranged plan for a suspected marauding terrorist.
It was not until two and a half hours after the blast Greater Manchester Police (GMP) officially declared the bombing a major incident.
2. Fire crews took more than two hours to attend
Station manager Andy Berry chose to mobilise resources three miles from the Arena amid fears over safety.
Sir John said: "The effect... was that the fire appliances at Manchester Central Fire Station drove away from, not towards, the incident.
"While driving away, the Manchester Central fire appliances drove past ambulances travelling in the opposite direction."
 PA
PA3. There were not enough paramedics
North West Ambulance Service (NWAS) did not deploy ambulances to the scene until nearly 30 minutes after the blast and there was only one paramedic at the scene for the first 40 minutes after the explosion.
Only three paramedics entered the City Room on the night to treat the dying and injured.
Sir John said more paramedics in the City Room would likely have identified the need for urgent treatment and/or evacuation, while more ambulances at the scene would also have meant quicker care.
Evacuation of casualties failed, with 36 people still waiting to be taken from the City Room past midnight.
4. Triage
There was a failure to send members of NWAS's specialist Hazardous Area Response Team into the scene of the explosion, to assist with triage and life-saving interventions with casualties.
Non-specialist paramedics were not sent into the area to assist with triage and there were not enough stretchers to help evacuate the injured.
Greater Manchester Fire and Rescue Service (GMFRS) did not arrive on scene and make any contribution to removing the injured.
5. There could have been more survivors
Sir John said the evidence was "conclusive" there was no possibility that 20 of the 22 victims could have survived the "murderous actions" of Salman Abedi, but John Atkinson's injuries were survivable "had he received the care and treatment he should have".
He said: "In the case of Saffie-Rose Roussos, it is highly unlikely that she could have survived her injuries.
"There was only a remote possibility she could have survived with different treatment and care."
 MAI
MAI6. Poor communication
There was a lack of communication between emergency responders, both through the act of physically co-locating at a single multi-agency rendezvous point and via radio.
There was no multi-agency control room talk group to allow control rooms to speak to each other directly.
No forward command post, for senior officers to liaise, was set up.
7. First aid training was inadequate
Manchester Arena operators SMG took an "unacceptable approach" to ensuring there were adequate healthcare services at the venue, the inquiry heard.
The company's then medical provider ETUK (Emergency Training UK Ltd), comprised mainly of first aiders, did not have "enough staff with necessary clinical qualifications, skills and experience on duty" on the night of the attack.

Why not follow BBC North West on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram? You can also send story ideas to [email protected]
