Phone scammers: 'Give me £1,000 to stop calling you'
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesWhen my landline rings (yes, I still have a landline), it is only ever going to be either my mum, my mother-in-law or a scam caller.
These days, the mum chats are far outnumbered by the scams.
Last week, fed up with their frequency, I asked the caller, who claimed to be from Microsoft's technical department, where she had got my number. "Take me off the list," I asked.
"Give me £1,000 and I will," she replied.
It felt like an audacious new low for an industry that already seems to be getting out of hand.
And for some, such calls are a lot more than just a nuisance.
One woman had a mobile call telling her that there was an ongoing court case against her over an unpaid tax bill. The judge and jury were on the line, the scammer told her, but if she immediately transferred payment of £999, the case would go better for her.
She panicked and paid but was told it was not enough. So she went to the bank, with the scammer still on the line, and sent another £4,000.
"As soon as she had done it, she realised it was a scam," said Louise Baxter-Scott, head of the national Trading Standards scam team.
According to Trading Standards, there has been a surge in such calls during lockdown.
"Everyone is at home so they are easy prey," said Ms Baxter-Scott.
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesAnd the scams are getting more sophisticated and more threatening.
One currently doing the rounds, purporting to be from the National Crime Agency, claims there is a warrant out for your arrest for "serious offences".
Another common claim is that National Insurance numbers have been stolen, which might seem plausible given the number of data thefts.
Although the request to immediately send money to the tax office should ring alarm bells.
Increasingly the calls are coming through to people's mobile phones, often appearing as a UK number to add another layer of legitimacy.
The top three problems Trading Standards identified were:
- people selling insurance for white goods, offering cover for fridges, freezers and washing machines
- impersonation callers claiming to be from the NHS, BT, Amazon or utility firms
- domestic home repairs such as boiler services and drainage
Some of these are defined as nuisance calls because they are actually selling something - albeit it something you probably do not need. Others are out-and-out scams.
People are thought to receive an average of seven scam or nuisance calls per month.
Scammers are particularly targeting the elderly.
Blocking calls
Trading Standards provided 2,000 call-blocking devices to people's homes to test their effectiveness at preventing the calls and to provide intelligence about the perpetrators.
The trial suggested such technology blocked more than 90% of unwanted calls.
Stevie Corbin-Clarke, a research assistant at Bournemouth University, worked on the project to understand the effect scams have on the public.
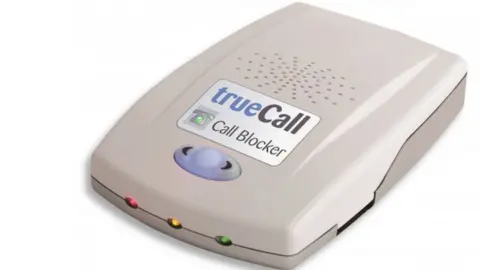 trueCall
trueCallHer research concluded that receiving scam and nuisance calls had a significant effect on people's wellbeing.
All regular landline users were likely to benefit from having a call blocker and they should also be made available to vulnerable individuals, the research suggested.
Robocalls
Similar blockers such as YouMail exist in the US, where automated calls, or robocalls, are getting out of hand.
A Business Insider survey suggested that half of Americans reported receiving scam phone calls on their mobiles every day, with another quarter receiving them several times per week.
During February, 4.6 billion were made, according to YouMail's chief executive Alex Quilici.
"The 2020 pandemic closed call centres so there were fewer, but now everything is opening up and robocalls are back," he told the BBC.
So-called robodiallers, often located overseas, make millions of calls per hour.
"It costs almost nothing to make these phone calls and they don't need a lot of people to respond to make a profit," said Mr Quilici.
He described how one New York-based woman in her 60s lost her life savings - some $350,000 - to a tax office scam. A student in her twenties lost $40,000 to a language school fraud scheme.
YouMail is a free app, although the firm offers a premium paid-for service to small businesses, and so far 10 million have signed up.
In the long run, Mr Quilici believes the problem will become rather like email spam - it will reach a certain level of intolerability, forcing both technological solutions and consumers to change behaviour.
"That combination will work but it will take a long time," he said.
As part of the fightback, last year the US Department of Justice launched cases against five companies they alleged were gateway carriers - allowing hundreds of millions of robocalls into the US phone system.
Meanwhile in the UK last month, the Information Commissioner's Office issued fines amounting to £270,000 to two separate companies for making unlawful marketing calls to numbers registered with the Telephone Preference Service (TPS).
Just a month earlier it handed out £480,000 worth of fines to four other companies.
Despite the fines, which are not always paid, similar firms keep popping back up.
Ms Baxter-Scott thinks phone companies could do more "to block calls on their networks".
And she is hoping that the trial with call blockers can be extended to local authorities.
"It is proven that having a £100 call blocker reduces anxiety, insomnia and [boosts] wellbeing so it make sense to fund this," she said.
