Covid-19: Don't think pandemic is over, Whitty warns
 PA Media
PA MediaUnlocking too quickly would lead to a substantial surge in Covid infections, the UK's chief medical adviser says.
Prof Chris Whitty told MPs that would be dangerous and risk lives among the many vulnerable people not yet protected by the vaccine.
"A lot of people may think this is all over. It is very easy to forget how quickly things can turn bad," he said.
His comments come amid pressure from backbench Tories to ease lockdown more quickly, given the drop in infections.
The Covid Recovery Group, which includes over 70 MPs, has pushed the prime minister to relax more steps, more quickly.
Appearing before the Science and Technology Select Committee, Prof Whitty said: "Under all the scenarios, if we unlock very suddenly, all the modelling suggests we would get a substantial surge while a lot of people are not protected."
Meanwhile, the latest daily figures for Covid show 5,766 more cases have been identified, 590 new admissions made to hospital and 231 deaths recorded within 28 days of a positive test.
Figures published on Tuesday show that over the weekend the number of people in hospital with Covid-19 fell below 10,000 for the first time since 25 October. The latest figures, covering 7 March, show there currently are 9,418 people in hospital with coronavirus.
Why impact of vaccination is gradual
In his evidence to MPs, Prof Whitty set out why, despite the impressive vaccination rollout programme, there are still many people vulnerable to the virus.
It takes about three weeks to build up immunity following the first dose of the vaccine.
So only the first four priority groups - the over-70s, health and care staff and the extremely clinical vulnerable - will have developed significant protection at the moment.
Most Covid deaths have been in these groups. But nearly half of hospital admissions have been seen in the under-70s.
And most transmission was driven by younger people, who had more social contacts, Prof Whitty said.
So the UK's policy of focusing on older age groups means it will be some time before the vaccine rollout will have a significant impact on the virus's spread.
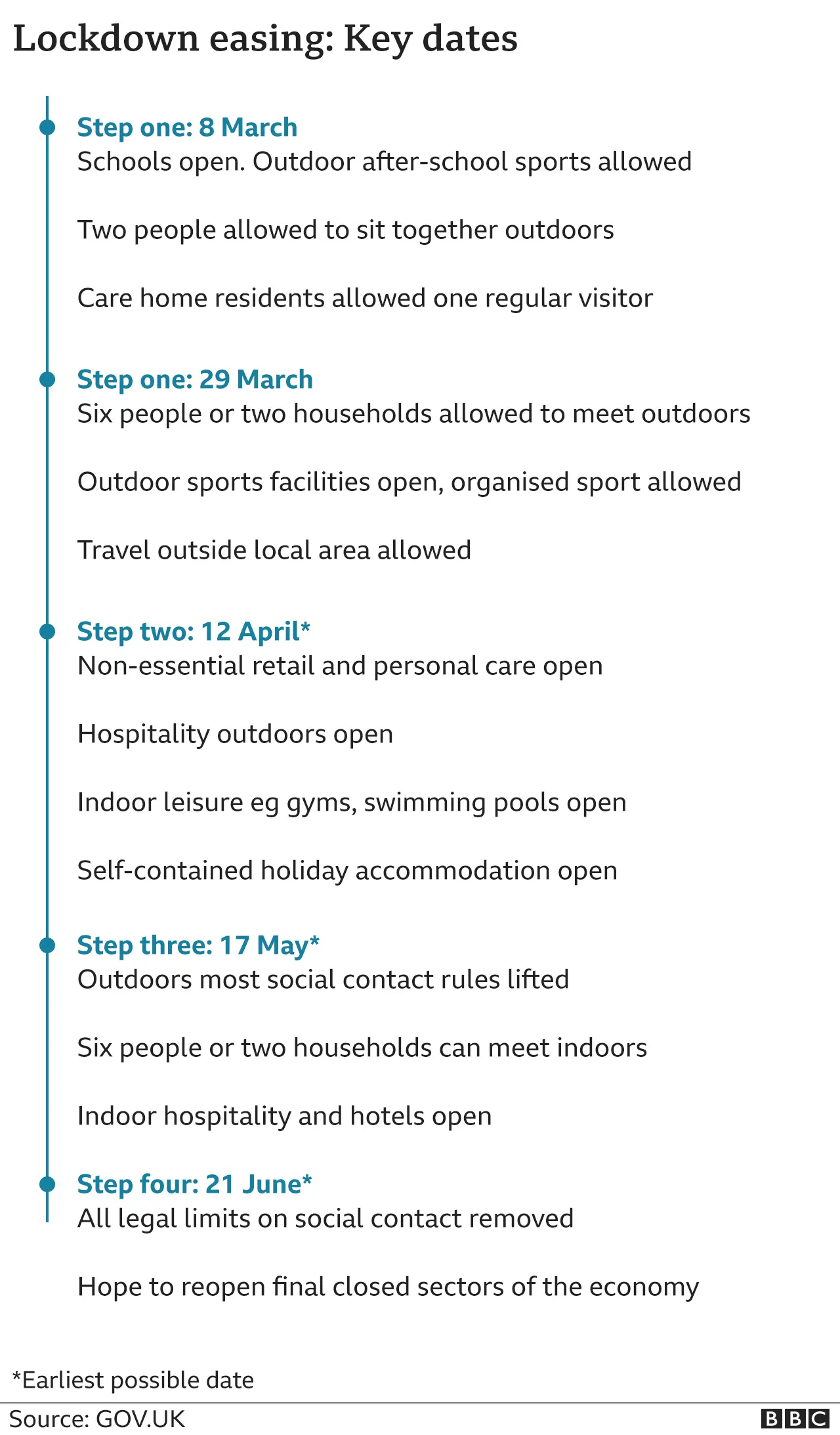

'You want to be confident each unlock is safe'
The step-by-step roadmap in England will not see all restrictions lifted until June at the earliest.
Prof Whitty said government advisers needed three to four weeks after a restriction was lifted to assess the impact.
And as the government wanted to give a week's notice of any changes to the roadmap, a five-week gap was needed.
"If you look at the steps, each one is quite a big one," he said.
"You want to be absolutely confident it is safe."

- LOCKDOWN RULES: What are they and when will they end?
- SYMPTOMS: What are they and how to guard against them?
- LOOK-UP TOOL: How many cases in your area?

He also said people who thought the UK was no longer at risk should look at continental Europe, with countries seeing rates going up and having to reintroduce restrictions.
Long-term 'people will still die of Covid'
Longer term, Prof Whitty said, it was unrealistic to expect zero deaths.
Even with a gradual lifting of restrictions, modelling suggests, there could be another 30,000 deaths before the summer of 2022.
This was because while the vaccines were good, Prof Whitty said, they were not 100% effective and with some people refusing to have them a proportion of the population would remain unprotected.

It was impossible to predict exactly how many would die, Prof Whitty said.
He said it would be a "significant number", though nothing like we had seen over the past year.
"The ratio of cases to deaths will go right down as a result of vaccination - but not right down to zero unfortunately," he said.
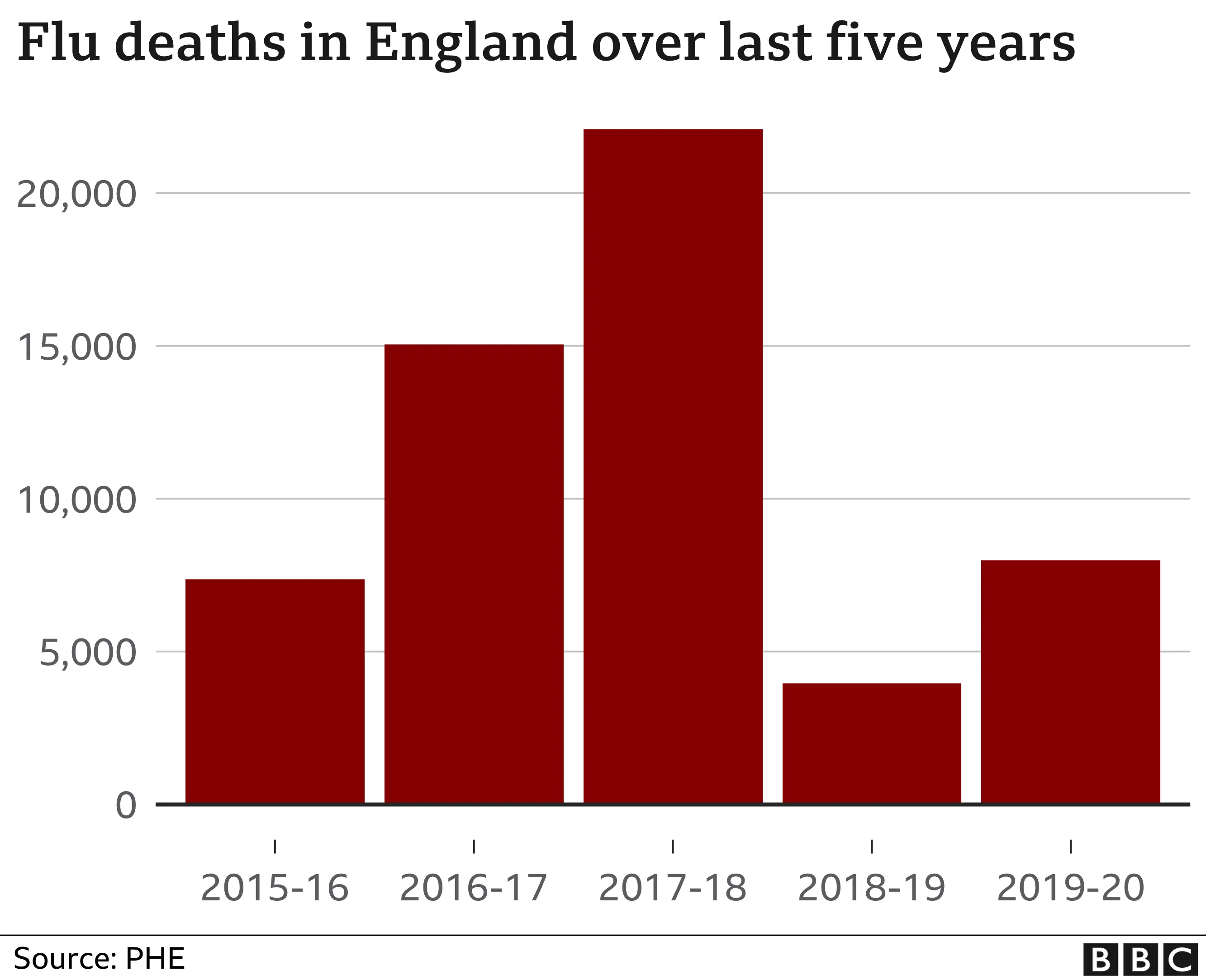
But he pointed out this was already the case for flu, saying in a bad winter 20,000 people could die.
And while Covid was expected to become seasonal, with future surges in the autumn and winter, he could not rule out a rise in cases in the summer.
