Government is undercutting UK institutions, says former Bank governor
Former Bank of England governor Mark Carney has accused the government of "undercutting" the UK's key economic institutions.
Mr Carney told the BBC the government's tax-cutting measures were "working at some cross-purposes" with the Bank.
He also pointed to a decision not to publish economic forecasts by the Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR) alongside Friday's "mini-budget".
The mini-budget sparked turmoil on financial markets and hit the pound.
Investors had been demanding a much higher return for investing in government bonds, causing some to halve in value. Pension funds, which invest in bonds, were forced to start selling, sparking fears of a fresh market downturn.
The Bank of England was forced to step in to calm markets and on Wednesday, said it would buy £65bn of government bonds over the next fortnight in an attempt to restore stability.
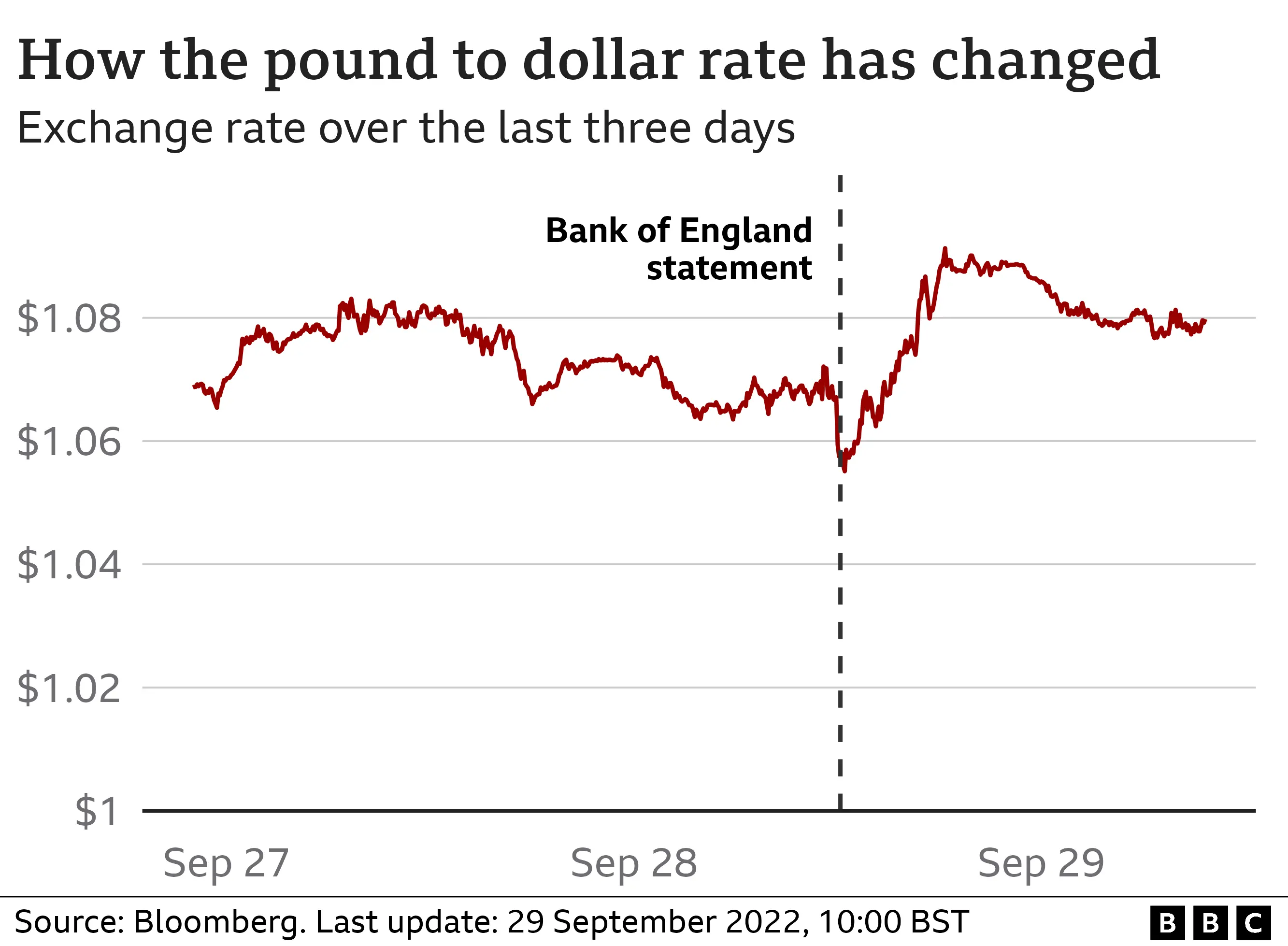
Sterling hit a record low against the US dollar of around $1.03 on Monday. It has since risen to around $1.08 after the Bank's announcement and remained there after Prime Minister Liz Truss said she would stand by the measures announced in the mini-budget.
The cost of government borrowing, however, edged higher and the interest paid - or yield - on 10-year government debt rose.
Speaking to the BBC's Today programme, Mr Carney said that while the government was right to want to boost economic growth: "There is a lag between today and when that growth might come."
He said: "There was an undercutting of some of the institutions that underpin the overall approach - so not having an OBR forecast is much-commented upon and the government, I think, has accepted the need for that but that was important."
The OBR provides independent forecasts of the impact of government's plans on the economy as well as on public finances. The Treasury decided not to publish its forecasts on Friday, which fuelled market turmoil.
"Unfortunately having a partial budget, in these circumstances - tough global economy, tough financial market position, working at cross-purposes with the Bank - has led to quite dramatic moves in financial markets," Mr Carney said.
The Treasury has subsequently said the OBR will release a full forecast when Mr Kwarteng announces his medium-term fiscal plan on 23 November.
Mr Carney also said that the government's mini-budget showed it was "working at some cross-purposes with the Bank in terms of short-term support for the economy".
Chancellor Kwasi Kwarteng unveiled the country's biggest tax package in 50 years on Friday. But the £45bn-worth of tax cuts has sparked concerns that government borrowing could surge along with rising interest rates.
The Bank has a target to keep inflation at 2%. But prices are rising at their fastest rate in four decades and the Bank has been lifting interest rates to cool inflation.
Since the mini-budget, some economists believe interest rates could rise faster and higher, to as much as 6% by next May.


At the helm of the Bank of England until 2020, Mark Carney was charged with rebuilding the reputation of British financial systems after the crash of 2008.
While it is not usual for former governors to comment on current issues, his stark words will be a further blow to the government as it defends its tax cuts. Mr Carney has indicated that the fall-out from these plans, by contributing to market turmoil, has consequences that may damage rather than enhance prosperity.
The Bank of England has been forced to inject billions of pounds into bond markets. That is after a plunge in their value threatened the viability of the pensions funds that manage workers' retirement pots.
During times such as the the financial crisis to the pandemic, the Bank of England has, on occasion, provided emergency help to ease global shocks. Doing so to offset the consequences of domestic government policy is far more rare.
With the markets remaining uneasy, analysts say an emergency interest rate hike can't be ruled out.

Ms Truss insisted that the government's plan was "right".
In her first remarks since Friday's announcement, Ms Truss told the BBC: "Of course there are elements of controversy, as there always are."
But she said: "This is the right plan that we've set out."
On Wednesday, Treasury Minister Andrew Griffith said that every major country "is dealing with exactly the same issues" as the UK such as Russia's war with Ukraine and the effect on energy prices.
But while Mr Carney conceded that the global economy is "going through some difficulties", he said that over the last week "developments have centred around the UK" and that recent financial turmoil was a response to the government's mini-budget.
Mr Carney was the governor of the Bank of England for almost seven years, from July 2013 to March 2020.
Before that he led Canada's central bank for five years, where he is seen as having played a major role in helping the country avoid the worst effects of the 2008 global financial crisis.
His successor as governor, Andrew Bailey, declined to comment on Thursday on whether the Bank would make further interventions.
Some economists - including former deputy governor Sir Charlie Bean - suggested that the Bank's Monetary Policy Committee call an emergency meeting and raise interest rates before a scheduled meeting on 3 November,
Mr Carney said it was "important that the system functions" but added: "We're talking about an interest rate meeting five weeks from now and it is important to see the persistence of the exchange rate moves, it is important to see what else the government does and take that into account."
He added: "This is a robust system, this is a resilient system, it has had a big knock but it will move forward."
The Bank is widely expected to raise interest rates before Mr Kwarteng announces his fiscal plan in late November.
This should set out how the government intends to follow its own fiscal rules. The current fiscal rules state that debt should be falling as a share of the UK's gross domestic product - which is all the goods and services that the country produces - by 2024-25.
The rules also dictate that by that same financial year, daily public spending should be balanced by revenues.
But it is possible that Mr Kwarteng could set out his own rules in November, changing those drawn up by his predecessor Rishi Sunak in November 2021.
