Kosovo: Why is violence flaring between ethnic Serbs and Albanians?
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesThe US says Serbia has sent a "large military deployment" of tanks and artillery to its border with Kosovo, and is urging its government to withdraw them.
This follows a clash last week between about 30 Serb gunmen and police officers in northern Kosovo.
The UK is sending 200 more troops to reinforce Nato peacekeepers in Kosovo.
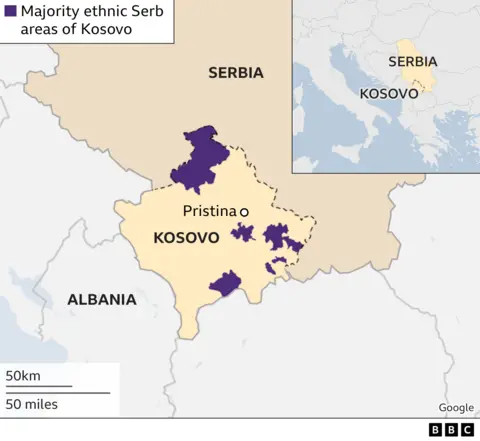
Where is Kosovo and who lives there?
Kosovo is a small, landlocked country in the Balkans in southern-eastern Europe. It borders Albania, North Macedonia, Montenegro and Serbia.
Many Serbs consider it the birthplace of their nation.
But of the 1.8 million people living in Kosovo, 92% are Albanian and only 6% Serbian. The rest are Bosniaks, Gorans, Turks and Roma.
How did Kosovo gain independence?
After the break-up of Yugoslavia in the 1990s, Kosovo - a province of the former country - sought independence.
Serbia responded with a brutal crackdown against ethnic Albanians.
This ended in 1999 with a Nato bombing campaign against Serbia, between March and June.
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesSerbian forces withdrew from Kosovo - but for many Kosovo Albanians and Serbs, the conflict has never been resolved.
The Nato-led Kosovo Force (KFor) is still based in Kosovo, with a current strength of about 4,500.
In 2008, Kosovo unilaterally declared independence.
A total of 99 out of 193 United Nations (UN) countries now recognise Kosovo's independence, including the US, the UK and 22 out of 27 European Union (EU) countries.
But Russia and China, which do not, have blocked Kosovo's membership of the UN.
And Serbian President Aleksandar Vucic has vowed Serbia would never recognise Kosovo as independent.
Neither Kosovo nor Serbia are in the EU, but:
- Serbia has been an EU candidate country since 2012
- Kosovo formally applied to join the EU in December 2022
The process of becoming an EU member can take decades.
Why has trouble flared up now?
A clash occurred in late September when ethnic Serb gunmen stormed the village of Banjska in the Serb-majority region of north Kosovo, barricading themselves in a Serbian Orthodox monastery.
One policeman and three gunmen were killed.
It is seen as the worst escalation of violence in years.
 Reuters
ReutersAt the heart of the violence is the Kosovo government's policy to assert authority over all of Kosovo.
Ethnic Serbs oppose this and also want more autonomy.
In 2022, Serb representatives in the north of the country resigned in protest against a ban on Serbian-issued number plates.
Following the resignation, local elections were held in April 2023 but were boycotted by a majority of the Serb population.
Four ethnic Albanian mayors were elected on a turnout of less than 4%. The mayors were installed by armed Kosovo police, provoking violent clashes with local Serbs.
Nato sent an additional 700 troops to the country, after some of its peacekeeping soldiers were injured in the clashes.
In October, about 200 UK troops will reinforce the existing Nato force in Kosovo, which consists of around 4,500 troops.
 Getty Images
Getty Images